Adenoidid refers to the inflammation of the adenoids. While this condition is typically seen in children, it can also present in adults. It usually brings discomfort in the form of nasal blockage, breathing difficulties, and even sleep disturbances. Even though the name may sound alarming, in most cases adenoidid is benign and quite manageable especially when detected early. In this article, we will talk about adenoidid, its causes, treatment options and diagnosis. We will explore its symptoms and the reasons behind them and whether it poses the risk of chronic ramifications, all explained in accessible language.
After reading this article, you should understand what adenoidid is, how it is expressed in the human body, and what you should do to manage it. As a parent or caregiver, or anyone else seeking to learn about this medical condition, the information presented will be trusted and pertinent.
What is Adenoidid?
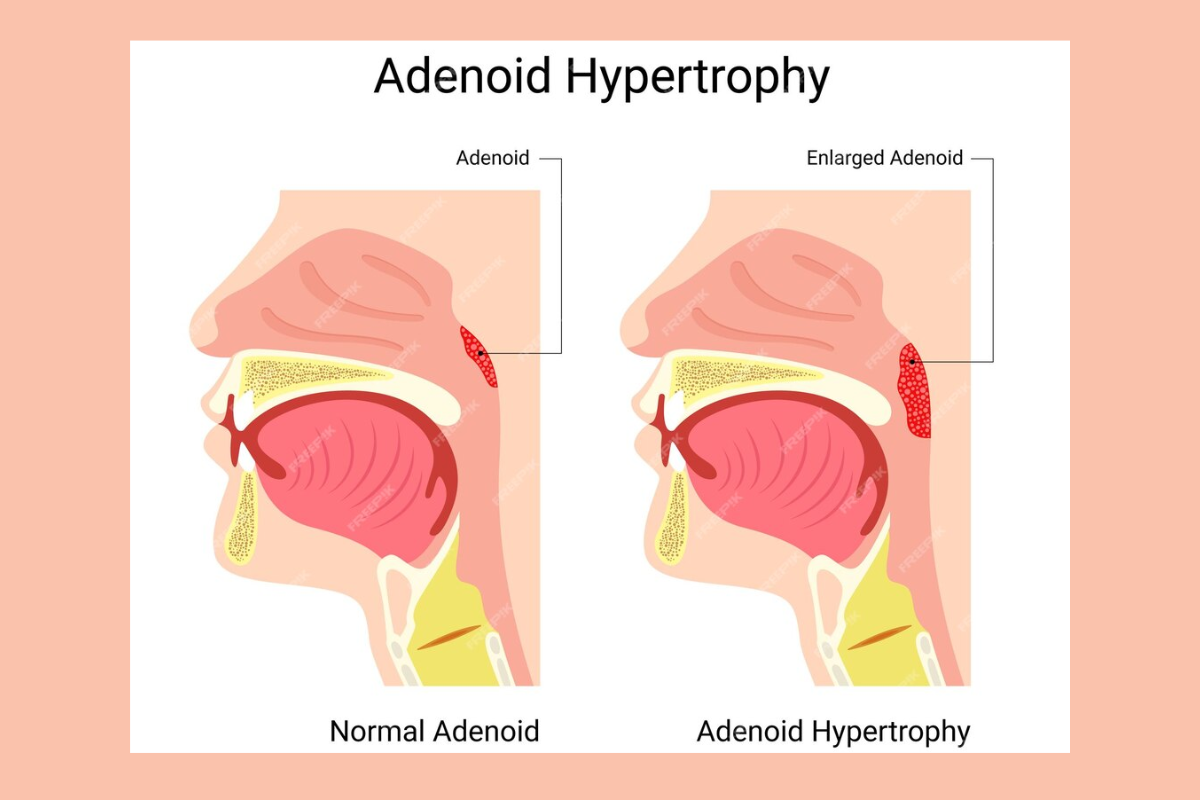
Adenoidid refers to the inflammation of the adenoids which are small patches of immune tissues situated at the back of the nose just above the mouth’s roof. Adnoids form part of the body’s immune system and help capture pathogens which enter through the nose and mouth. When the adenoids are infected or irritated, there is inflammation of the adenoids which is known as swelling.
The condition is akin to the infection of the tonsils, however it affects a different region of the upper throat. In most instances, adenoidid is either viral or bacterial. It can be acute or chronic. In cases of acute adenoidid, the condition manifests suddenly. On the other hand, chronic adenoidid persists for weeks or recurrently manifests over time.
Grouped under a single keyword, adenoidid pertains to a certain form of inflammation. This does not refer to the condition known as enlarged adenoids, although in both cases some degree of swelling is present.
Common Symptoms of Adenoidid
Adenoidid stems from a number of distinct symptoms, some of which tend to differ with respect to age and severity of inflammation.
Symptoms in Children
The condition adenoidid is more prevalent in children due to their larger and more active adenoids relative to adults. Common symptoms include nasal obstruction, mouth breathing, snoring, and disrupted sleep. Children exhibiting symptoms of adenoidid may also exhibit a nasal voice and increased drooling. Additionally, they may experience sore throats, earaches, or even difficulty in swallowing.
It is particularly critical for parents to identify these symptoms. Untreated adenoidid can disrupt a child’s sleep and cause recurrent ear infections or chronic sinusitis.
Signs to Watch for in Adults
While it is uncommon, there are some reported cases of adult adenoidid. Its symptoms often manifest as persistent nasal congestion alongside post-nasal drip, halitosis, and recurrent pharyngitis. Chronic sufferers of adenoidid often experience cephalalgia or sinus pressure. Although adenoidid is less common among adults, it remains important to diagnose and treat.
Causes and Risk Factors of Adenoidid
Knowing the possible causes of adenoidid can aid in its prevention or mitigation. This condition is more often resultant from infections as well as other irritative processes.
Bacterial versus Viral Infections
A viral infection, such as the common cold or flu, is the most typical cause of adenoidid. Such viruses gain entry through the nose or mouth and localize to the adenoids. Adenoidid may also arise from bacterial infections like Streptococcus. Such infections would require antibiotic therapy for resolution.
Children in daycare or school settings have higher exposure to pathogens, predisposing them to adenoidid.
Other Contributing Conditions
Chronic adenoidid may stem from the repeated infections due to significantly enlarged adenoids. Other risk factors include asthma and chronic sinusitis. Environmental factors like smoke and pollution, as well as allergies, can also exacerbate the condition.
Chronic adenoidid may be further complicated by inadequate hygiene and weakened immune defense mechanisms.
Management of Adenoidid
A physician will usually start the encounter with a physical examination, focusing on the head and neck region, including the nasal passages. Detection of symptoms such as snoring or nasal obstruction will be further explored. Given that adenoids cannot be assessed directly via oral examination, endoscopic visualization or imaging like X ray of the nasopharynx is performed.
Throat swabs and blood tests may be performed in specific situations to determine the type of infection present. A timely and precise diagnosis aids in effective treatment which in turn accelerates recovery.
Adenoidid Treatment Methods
The method of treatment prescribed for adenoidid varies according to its cause and severity. In many instances, it resolves spontaneously with conservative measures. In other cases, intervention might be necessary.
Self-Care and Home-Based Relief Methods
Generally, self-care is effective for mild cases of adenoidid. The symptoms may be alleviated by ensuring adequate fluid intake, rest, and the use of a humidifier. Symptoms can also be comforted by warm saltwater gargles and saline nasal sprays.
Environmental factors are also important, including the clean air. Avoiding allergens and cigarette smoke is vital. Maintaining hygiene and keeping the nostrils clear can bolster the recovery process.
Pharmaceutical Therapy and Surgical Treatment
Should adenoidid be secondary to a bacterial infection, the physician will likely initiate treatment with antibiotics. These medications decrease bacterial proliferation and resulting inflammation. Occasionally, steroid nasal sprays may be utilized to reduce the size of the inflamed adenoids.
Pain or fever may be managed with acetaminophen or ibuprofen. These medications may also be used to manage pain associated with adenoidid. Dosage for children should be in accordance with the physician’s guidance.
Surgical Considerations
In cases where adenoidid is persistent or is associated with complications such as ear infections or sleep apnea, surgery may be an option. This procedure is known as an adenoidectomy, which involves complete removal of the adenoids.
This is commonly performed on children, and is considered a safe procedure. Recovery time is quick, and the vast majority of people improve within a week.
Can Adenoidid Cause Long-Term Problems?
Although most cases of adenoidid resolve spontaneously, some may lead to long-term issues if left inadequately managed.
Effects on Breathing and Sleep
Enlarged or inflamed adenoids can impede the airflow through the nose while making breathing laborious, especially during sleep. Children may exhibit snoring or apneic episodes, a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing. Sleep disruption can have negative consequences on a child’s growth, behavior, and cognitive function.
Recurrent Infections and Their Consequences
Frequent episodes of adenoidid may result in chronic infections of the ear or sinus. This may lead to hearing loss or delay speech development in children. Thus, appropriate management of adenoidid is imperative in preventing these complications.
For adults, long-term adenoidid may worsen chronic sinus congestion, fatigue, or halitosis, thereby diminishing quality of life.
Conclusion
Adenoidid poses discomfort, yet typically can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment. Early recognition of the symptoms and obtaining appropriate medical consultation can prevent complications and significantly enhance recovery. In most cases, both children and adults will find the treatment to be straightforward. Easing measures exist, including home treatments, pharmaceuticals, or minor surgical interventions which address the condition before it leads to significant complications.
Equipping oneself and parents with the knowledge of the causes, symptoms, and treatment of adenoidid enables timely intervention. With proactive measures such as promoting good cleanliness, monitoring for specific symptoms, and avoiding bothersome factors, profound improvement can be noted. This condition, with appropriate management, can be rendered non-disruptive.
FAQs
What is the difference between adenoidid and tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis and adenoidid share the same inflammatory nature, although the former affects the tonsils while the latter involves the adenoids. Both structures belong to the lymphatic system and serve to protect the body from pathogens. Though they can occur concomitantly, they remain distinct.
Can adults get adenoidid or is it only a childhood issue?
Although adenoidid is primarily pediatric, it can also present in adults. That said, adult cases are much less common and tend to be associated with chronic disease states like infections or allergies.
What is the typical duration of adenoidid?
Acute cases of adenoidid resolve in one to two weeks, but chronic cases may persist or relapse multiple times. Effective management and accurate diagnosis can diminish the duration and severity of symptoms.
Is surgical intervention frequently indicated for chronic adenoidid?
No, surgical intervention is not frequently indicated for chronic cases. It is often suggested only when there is frequent recurrence of symptoms or issues like ear infections and sleep apnea.
My name is Mustafa, and I have been blogging for over 5 years. I am passionate about sharing complete, accurate, and helpful information with my readers. Along with managing content on The Matcha Read, I also contribute blog posts to premium websites. My goal is to provide valuable insights in a clear and easy-to-understand way, so every reader walks away with useful knowledge.